Hot to take phentermine 37.5 for best results
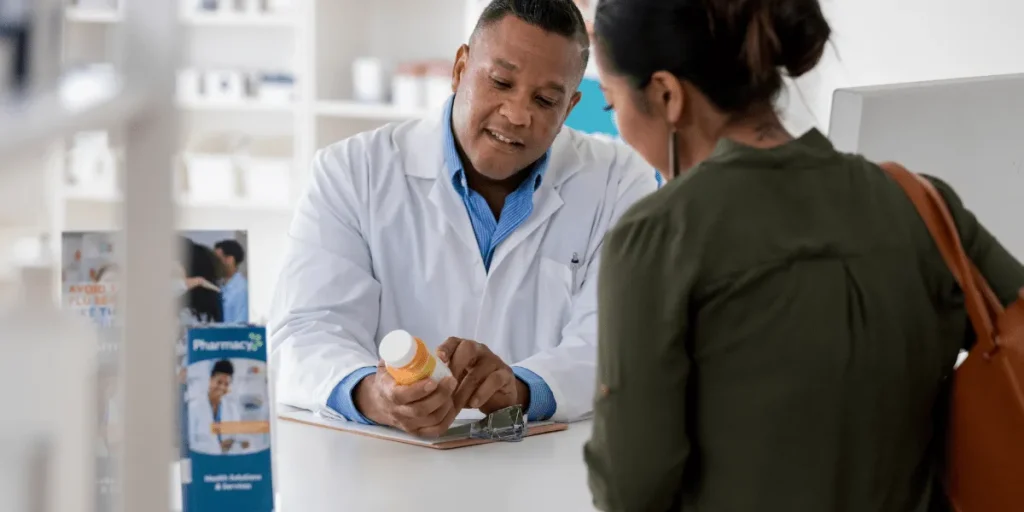
How to take phentermine 37.5 for Best resultsIntroduction to How to take phentermine 37.5 for best resultsPhentermine 37.5 should be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Generally, it is taken once a day in the morning, about 30 minutes before breakfast or 1-2 hours after breakfast. Taking it before breakfast may maximize its effectiveness, but it’s essential to follow your doctor’s specific instructions for dosing and timing.Avoid taking Phentermine 37.5 in the evening or close to bedtime to prevent insomnia and other sleep disturbances. It is crucial to follow the dosing schedule provided by your healthcare provider to ensure the medication’s safe and effective use.Remember that the recommended dosage and timing may vary from person to person based on individual health conditions and needs. Always consult your doctor before making any changes to your dosing or timing. It’s important to use Phentermine 37.5 as directed to achieve the best results and minimize the risk of side effects.Phentermine Dosages for Weight Loss: Your GoodRx GuideWhen it comes to weight loss, finding the right medication and dosage is crucial. Phentermine is a popular prescription medication used to aid weight loss by suppressing appetite and boosting energy levels. Finding the right Phentermine dosage for your body and weight loss goals can be a game changer in your journey to a healthier you. In this guide, we’ll explore the different Phentermine dosages available and how to effectively use this medication as a tool for weight loss. Whether you’re new to Phentermine or looking to adjust your current dosage, this GoodRx guide will provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your weight loss journey.How to use Phentermine HCLPhentermine HCL should only be used as prescribed by your doctor, taking into consideration your age, medical condition, and how you respond to the medication. Typically, Phentermine HCL is taken once a day with breakfast. It is important not to crush or chew sustained-release capsules, as this can affect the way the medication is released in your body.Swallow the medication whole with a full glass of water and take it at the same time each day to get the most benefit. It is important to not increase your dose, take it more often, or use it for longer than prescribed. If you have any questions about the dosage or administration of Phentermine HCL, be sure to consult your doctor or pharmacist.Always read and follow the medication guide provided with Phentermine HCL. If you have any concerns or experience any adverse effects while using the medication, contact your healthcare provider immediately.Proper Use of Phentermine tabletsPhentermine is a prescription weight loss medication that works by suppressing the appetite and boosting energy levels. When used properly, Phentermine can be an effective tool in conjunction with diet and exercise to help people achieve their weight loss goals. However, it’s important to use Phentermine tablets as directed by a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects and to maximize its benefits. Understanding the proper use of Phentermine tablets is crucial for safe and effective weight loss.DescriptionsPhentermine Hydrochloride Tablet, USP is available in oral dosage form. It contains the active ingredient Phentermine Hydrochloride, which is a sympathomimetic amine anorectic. The chemical composition of Phentermine Hydrochloride Tablet, USP is C10H15N•HCl.Phentermine Hydrochloride is sparingly soluble in water and ethanol. The tablet is typically white or off-white in color, round in shape, and may have a score line for ease of splitting. The tablet may also be imprinted with a specific identification code.In addition to the active ingredient, the tablet also contains inactive ingredients such as lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, pregelatinized starch, and sucrose. These inactive ingredients contribute to the physical characteristics of the tablet and help in its formulation.Overall, Phentermine Hydrochloride Tablet, USP is available in oral dosage form and contains the active ingredient Phentermine Hydrochloride. It is sparingly soluble in water and ethanol, and its physical characteristics include a white or off-white color, round shape, and specific identification markings. Its formulation includes various inactive ingredients to aid in its production and stability.DosingOptions for Obesity Treatment:The dosing options for the treatment of obesity include various dosage forms such as oral tablets, capsules, and injections. The recommended doses and administration timings vary depending on the specific medication and the individual’s weight management plan.For adults, the recommended dose for oral medications is usually once daily, with or without food, while some injectable medications may be administered weekly. The specific dosage form and strength will determine the exact recommended dose, which can range from 1-3 capsules or tablets per day.For children, the recommended doses are determined based on their age, weight, and the specific medication prescribed by a healthcare professional. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage for children.The maximum dosage and frequency of use for weight loss medications are typically outlined in the prescribing information. It is important to adhere to the recommended maximum dosage and frequency to avoid potential side effects and adverse reactions. The timing of medication administration in relation to meals may also vary, with some medications being taken before, during, or after meals.In summary, the dosing options for obesity treatment depend on the specific medication, and it is important to follow the recommended doses and administration timings provided by a healthcare professional.Specific UsesPhentermine is a medication used to aid weight loss in individuals who are obese or have weight-related medical problems. It is available in various dosage forms, including capsules, tablets, and extended-release capsules, and should be taken as directed by a healthcare provider. The typical adult dose is 8 mg to 37.5 mg once daily, with or without food.It is crucial to follow the dosing instructions for the specific form of phentermine being used, as well as to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet plan and regular exercise program. The combination of medication, diet, and exercise is essential for achieving successful weight loss. Before starting an exercise program, it is important to consult with a doctor to ensure